Geothermal heating
Geothermal energy can come in different shapes; deep or shallow, high or lower temperature and be used for electricity or heat generation - but have always in common that it is available 24/7. Because it comes from the earth’s crust it is a renewable source that is not dependent on weather or season. Apart from heating, an aquifer storage system can also be used to deliver free cooling to a building.
Choose the right Geothermal Energy partner
- At Alfa Laval, we see the great potential in geothermal energy being an important sustainable heating resource for the future.
- Our goal is to supply energy efficient and reliable solutions that facilitate the highest possible yield at the lowest cost to the environment.
- With nearly 100 years of heat transfer experience and service centers all over the world, We have experience and local presence in all the markets.
- We know which heat exchanger will best optimize your production with the lowest possible payback time.
- With AHRI third party performance certification, you can rest easy that the thermal performance of our products is as good as we say it is.
Trends in geothermal heating industry
Focus on geothermal energy as an alternative to traditional fossil fuels is on the rise in the heating sector. Especially where it can replace fuels in district heating networks and reach a large number of customers from one single set of wells. There is also a growing experience for use of shallow geothermal with lower available temperature and aquifer thermal storage systems together with heat pumps to form a affordable and energy efficient options on the renewable energy market.
However, this industry doesn’t come without challenges. As the water can contain high levels of chloride and other impurities, scaling and fouling can build up and reduce the performance of process equipment. That is where we come in. Alfa Laval’s high-quality equipment and experience in the field of service are proven to keep your processes at optimum capacity with minimal downtime.

When it comes to equipment, we simply have to pick the best. The supplier must be able to prove a powerful capacity for after sales services and emergency preparedness. We are happy to say, that Alfa Laval fulfils these uncompromising criteria with a very safe margin.
Ali Ichedef, General Manager of Izmir Jeotermal
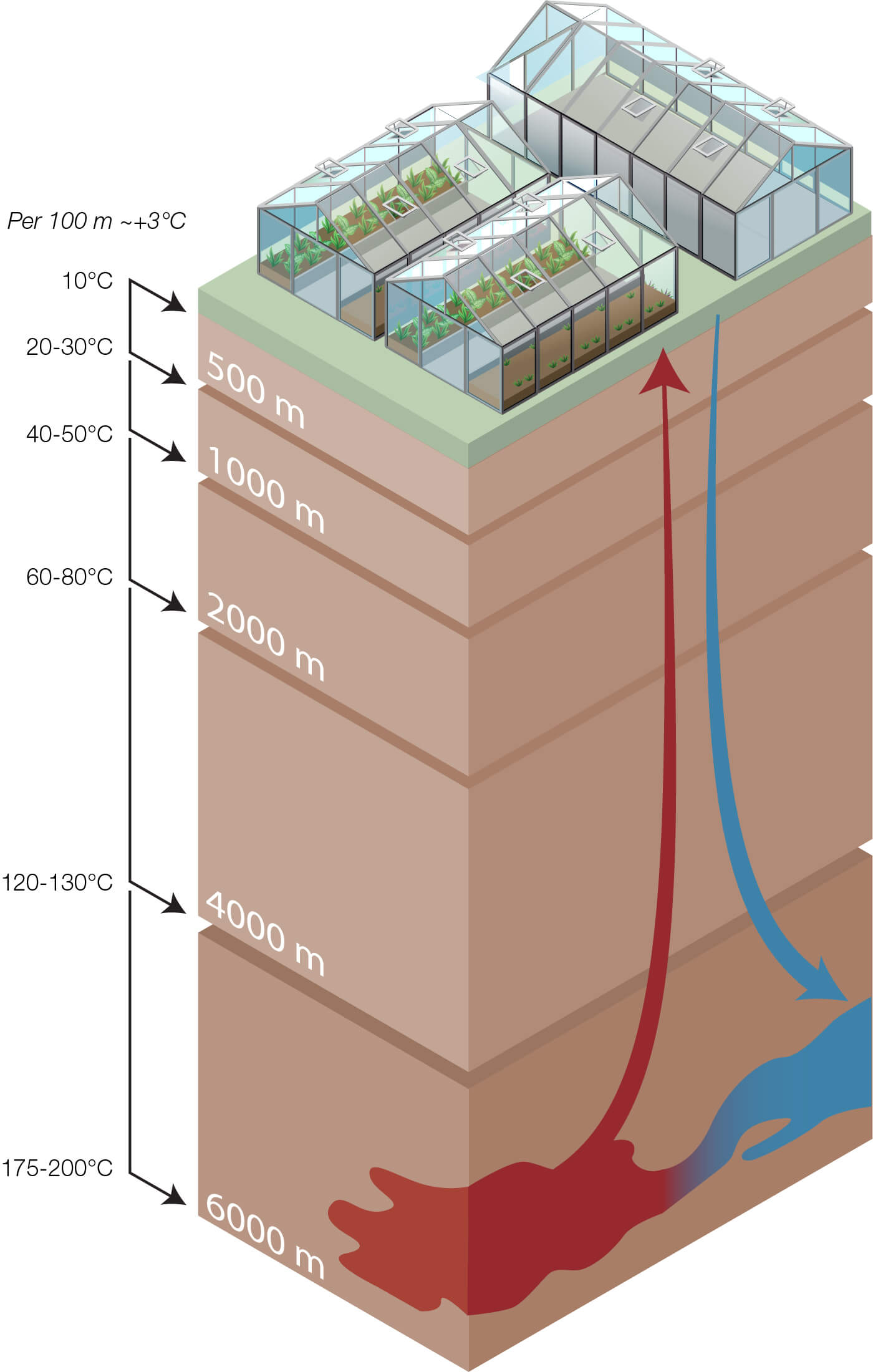
The Geothermal temperature gradient depends on the depth of the well together with the location. Some locations can have higher temperatures close to surface level, for example, Iceland. However, most locations have a temperature range illustrated by the graph.
Geothermal heating works by extracting the heat from an underground water source. The further underground the water is extracted, the hotter it usually is. In the Netherlands, geothermal heat plants pump warm water from depths of at least 500 meters. When heat has been drawn from the geothermal water it is returned to the ground in the injection well.
The Netherlands is the world’s second-largest food exporter by value, and the country’s 9000 hectares of greenhouses are a big reason why. But keeping those greenhouses at the right temperature requires lots of energy, so developing alternative energy sources is a top priority in the country’s efforts to meet its ambitious climate targets.
Heat exchangers play a key role in harnessing the benefits to geothermal energy, ensuring efficient heat transfer between the warm water coming up from the ground and the cooler water that has been used to heat greenhouses or other buildings.
Difference between shallow, aquifer and deep geothermal
Every well is unique with depths changing depending on location and conditions. When this industry talks about shallow or deep wells it is really to identify the main characteristics of a project. Shallow geothermal heat is generated from subsurface water using either an open loop where water is pumped from the well or a closed loop system with brine in a collector loop which is pumped up and down in the well.
Shallow wells and aquifers (<=500m)
Shallow geothermal heating, and ATES (aquifer thermal energy storage) is a renewable energy technology that uses the relatively constant temperature of the upper layers of the earth's crust to heat and/or cool buildings.
Unlike deep geothermal systems, shallow geothermal systems typically operate at depths of up to 100 meters.
Shallow geothermal wells generate a temperature level that cannot be used directly as it is – hence the absorbed heat in a shallow geothermal project is used together with heat pumps, which increases the temperature to a more useful temperature level for heating purposes. A shallow geothermal system can also be used in reverse where the water below ground is used as a free cooling source to cool buildings during hot weather.
Shallow geothermal systems are a popular choice for residential and small commercial buildings, as they can be installed in a relatively small space and require less drilling and excavation than deep geothermal systems.
Deep wells (2000 - 5000m)
Deep geothermal heating, is a renewable energy source that uses the heat which comes from the core of the earth.
The hot water and potentially even steam are brought to the surface and used to generate heat by running it through a heat exchanger where energy is transferred to the second level where it is distributed to the point where it is being used. From deed geothermal wells the temperature can be high enough to be used directly as it is. But at some locations and depths, there can still be a need for increasing the temperature level with heat pumps. It is quite common that deep geothermal sources are connected to a district heating system.
The depth at which deep geothermal systems operate can vary depending on several factors, including the geological characteristics of the area, the type of system being used, and the heat requirements of the buildings in which the heat is being used.
In general, deep geothermal systems operate at depths ranging from about five hundred meters to several kilometers below the surface. The most common depths for deep geothermal systems used for delivering heating to buildings and greenhouses are between 1,500 and 3,000 meters.
Gasketed plate-and-frame heat exchangers
- Flexible solutions that can be adapted to the duty ensuring highest thermal efficiency
- Compact designs save space and are easy to service and maintain
- Solutions to reduce fouling, stress and corrosion for maximum uptime
Semi-welded plate heat exchangers
- Highly efficient, reliable technology for applications that can cause pressure or temperature fatigue
- Guaranteed long sealing lifetime thanks to unique Alfa Laval RefTight™ sealing system
- A dependable solution for preventing cross-contamination between media
Brazed plate heat exchangers
- Lightweight copper-brazed construction with compact footprint
- Greater thermal efficiency than comparable shell-and-tubes
- Flexible options to fit a variety of applications with all different types of media/fluids
- Ideal for natural and low-GWP refrigerants
Fusion bonded AlfaNova heat exchangers
- True 100% stainless steel construction
- Strong corrosion resistance with aggressive media
- Prevents metal contamination in drinking water and other hygienic applications
- High thermal efficiency and compact footprint
AHRI-performance-certified heat exchangers for confident thermal performance
Certification from the Air-Conditioning, Heating, and Refrigeration Institute (AHRI) is the only global third-party verification of thermal performance, giving you independent assurance that your plate heat exchanger will perform in accordance with the manufacturer’s published ratings. Alfa Laval offers AHRI-certified gasketed plate heat exchangers, brazed plate heat exchangers, and fusion-bonded plate heat exchangers.

Consultant? System integrator?
Are you a consultant? Look here! With expertise from decades of experience in heat exchange, Alfa Laval offers knowledgeable resources for today’s heating and cooling challenges. Discover answers to complex questions on everything from energy efficiency to natural refrigerants, along with helpful tools that make it simpler to find the right technology for your application.

Making efficiency last for decades
A poorly functioning heat exchanger may affect safety, product quality and energy costs. Failure may lead to costly downtime and major losses in production. By regular and proactive maintenance of your gasketed plate heat exchanger performance is preserved and operations kept trouble-free and predictable.
We have the expertise to help you whether you experience a problem today, wish to prevent future issues or want to solve the problem yourself with our online troubleshooter.

Digitalization for energy efficiency
Smart cities and digital intelligence could help cities to make progress toward meeting 70 percent of their Sustainable Development Goals. Digital services can already have a significant impact on heating and cooling systems in cities, making them more sustainable.
Enabling remote monitoring and performing dedicated analytics allow more precise and efficient operation, more informed decision-making, and targeted interventions. The development of more sophisticated and efficient heating and cooling systems is only possible through this digital transformation, which can provide reliable and affordable heating and cooling services to urban areas while reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
HVAC and the Sustainable cities
Consuming more than two-thirds of the world’s energy, our cities play a crucial role in tackling the climate crisis. A considerable part of cities’ energy consumption is for heating and cooling, which means improving energy efficiency is paramount. Alfa Laval has almost a century of experience in heat transfer and recovery and aims to become carbon neutral by 2030. Let us be your partner in the transformation to a sustainable tomorrow.